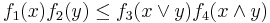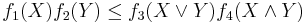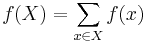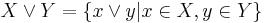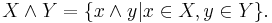Ahlswede–Daykin inequality
A fundamental tool in statistical mechanics and probabilistic combinatorics (especially random graphs and the probabilistic method), the Ahlswede–Daykin inequality (Rudolf Ahlswede & David E. Daykin 1978) is a correlation-type inequality for four functions on a finite distributive lattice.
It states that if ƒi, i = 1, 2, 3, 4 are positive functions on a finite distributive lattice such that
for all x, y in the lattice, then
for all subsets X, Y of the lattice, where
and
It implies the Holley inequality, which in turn implies the FKG inequality. It also implies the Fishburn–Shepp inequality.
For a proof, see the original article (Ahlswede & Daykin 1978) or Alon & Spencer (2000).
References
- Ahlswede, Rudolf; Daykin, David E. (1978), "An inequality for the weights of two families of sets, their unions and intersections", Probability Theory and Related Fields 43 (3): 183–185, doi:10.1007/BF00536201, ISSN 0178-8051, MR0491189
- Alon, N.; Spencer, J. H. (2000), The probabilistic method. Second edition. With an appendix on the life and work of Paul Erdős., Wiley-Interscience, New York, ISBN 0-471-37046-0, MR1885388
- Fishburn, P.C. (2001), "Ahlswede–Daykin inequality", in Hazewinkel, Michiel, Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1556080104, http://www.encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=a/a110440